Birthing positions play a vital role in ensuring a comfortable and effective labor experience. Upright and ambulatory positions utilize gravity to aid labor progression, while forward-leaning and asymmetrical positions can alleviate discomfort and facilitate baby movement. Understanding optimal positioning empowers women to make informed choices, enhancing both physical comfort and emotional satisfaction during childbirth.
Importance of Birthing Positions in Labor
Birthing positions significantly influence labor progression and comfort. Upright and ambulatory positions leverage gravity to facilitate fetal descent, while forward-leaning and asymmetrical positions can ease discomfort and improve pelvic alignment. These positions enhance mobility, allowing the baby to move more freely, which can reduce labor duration and intensity. Additionally, optimal positioning can help alleviate back pain and improve contractions’ effectiveness. By promoting comfort and reducing physical strain, birthing positions play a crucial role in empowering women and fostering a positive birth experience. Evidence supports the benefits of movement and positioning in improving labor outcomes, emphasizing the importance of informed choices for expectant mothers. Understanding these positions can help women feel more in control, reducing anxiety and fostering confidence during childbirth.
Overview of the Stages of Labor and Positioning
Labor is divided into distinct stages, each benefiting from specific positioning strategies; During early labor, walking, swaying, or using a birth ball can help contractions progress. As labor intensifies, active labor positions like forward-leaning or side-lying may reduce discomfort and enhance fetal movement. Transition, the most intense phase, often sees women resting or changing positions frequently to manage pain. The pushing stage offers various options, such as squatting or semi-sitting, to maximize pelvic space and leverage gravity. Each stage’s positioning is tailored to support physiological processes, ensuring the baby moves smoothly through the birth canal. Understanding these stages and their corresponding positions empowers women to navigate labor more effectively, fostering a more manageable and positive experience. By aligning positioning with labor’s progression, women can optimize comfort and support their body’s natural processes.
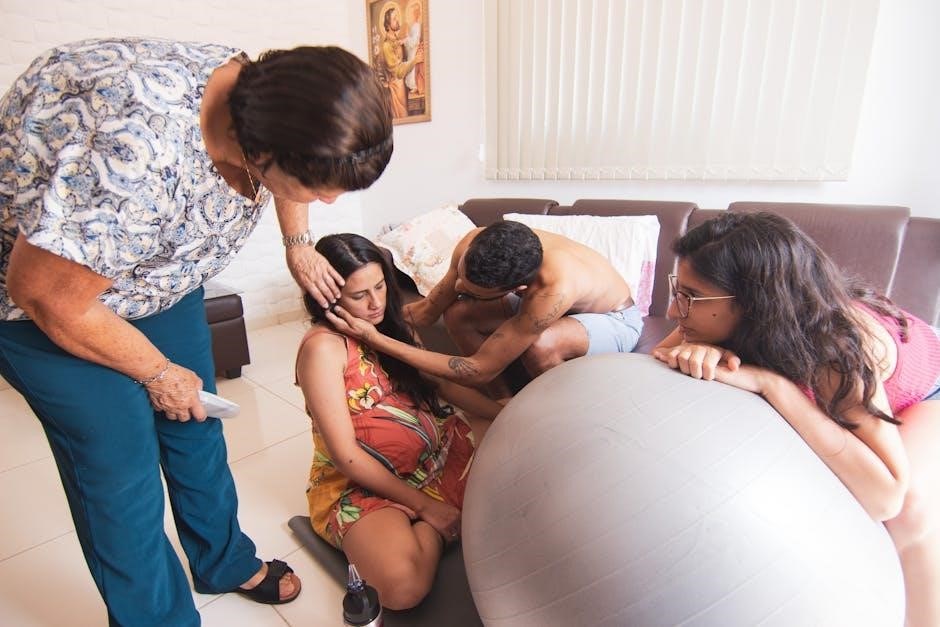

Optimal Birthing Positions for Each Stage of Labor
Each labor stage benefits from tailored positioning to enhance comfort and progression. Early labor favors walking or swaying, while active labor may involve forward-leaning or side-lying. Squatting during pushing maximizes pelvic space, leveraging gravity for efficient delivery.
Early Labor Positions
During early labor, staying upright and mobile is key to promoting comfort and progress. Walking and swaying can help the baby move down into the pelvis. Leaning forward, either against a partner or a pillow, can alleviate back pain and facilitate the baby’s rotation. Sitting on a birth ball is another effective position, allowing gentle pelvic rocking to ease discomfort. Side-lying or resting in a semi-sitting position can provide moments of rest while maintaining alignment. These positions encourage the baby to find an optimal position for delivery, utilizing gravity and movement to gently coax the baby down the birth canal. Remaining active and changing positions regularly helps maintain a sense of control and comfort during this initial phase.
Active Labor Positions

Active labor benefits from dynamic positioning to support progress and comfort. Squatting is effective for widening the pelvic outlet, while the hands-and-knees position can relieve back pain and help the baby rotate. Asymmetrical positions, such as standing with one leg elevated, allow the baby to move more freely. These positions leverage gravity and movement to facilitate the baby’s descent. Using support like pillows or a partner can enhance stability and comfort. Staying mobile during active labor helps maintain momentum and reduces discomfort, promoting a more manageable experience. Regularly changing positions can also prevent stagnation and support the baby’s optimal positioning for delivery. Balancing activity with rest is key to conserving energy while maintaining progress.
Pushing Positions
During the pushing phase, various positions can enhance comfort and effectiveness. Upright positions, such as squatting or standing, utilize gravity to aid the baby’s descent. The hands-and-knees position is ideal for relieving back pain and facilitating baby rotation. Side-lying positions allow rest while maintaining an open pelvis. Semi-sitting or leaning forward with support can also be beneficial. Each position offers unique advantages, such as widening the pelvic outlet or promoting fetal movement. Support from partners or pillows is crucial for stability. Freedom to move and change positions during pushing can improve outcomes and reduce discomfort. Evidence supports the use of upright and ambulatory positions to progress labor and enhance satisfaction. Ultimately, the choice of position should align with the mother’s comfort and the baby’s needs, ensuring an empowered and effective birthing experience.

Benefits of Upright and Ambulatory Positions
Upright and ambulatory positions leverage gravity to enhance labor progression, improve comfort, and reduce pain. They promote baby movement and alleviate back pain, supporting a more natural birthing process.
Gravity Advantage in Labor Progression
Upright and ambulatory positions harness gravity to facilitate labor progression, allowing the baby to move more easily through the pelvis. Standing, walking, or leaning forward enables the uterus to work more efficiently, often reducing the duration of labor. These positions help the baby descend and align properly, which can minimize the need for interventions;Gravity naturally assists in rotating and guiding the baby into optimal positions for birth, potentially reducing complications. Women who remain upright tend to experience shorter labors compared to those lying flat, as gravity aids in the baby’s movement down the birth canal. This natural assistance can lead to a smoother and more effective labor process, though individual circumstances may vary and medical guidance is essential. Upright positioning is a simple yet powerful tool to support labor progression and improve outcomes.
Improved Comfort and Reduced Pain
Upright and ambulatory positions significantly enhance comfort and reduce pain during labor. Walking, swaying, or leaning forward allows the mother to move freely, which can help alleviate discomfort and back pain. Using a birth ball is another effective strategy, as it supports the pelvis and lower back, enabling gentle movements that can ease tension. These positions also allow the baby to shift and move, which may reduce pressure on sensitive areas. By staying upright, women can change their posture to find relief and rest when needed. Forward-leaning positions, such as kneeling or resting on a pillow, can further alleviate back pain and provide a sense of control. Overall, these strategies empower women to manage discomfort and feel more comfortable throughout the labor process. Informed positioning choices can greatly improve both physical and emotional well-being during childbirth.
Enhanced Mobility and Baby Movement
Upright and ambulatory positions significantly enhance mobility and facilitate baby movement during labor. Walking, squatting, or using a birth ball allows the pelvis to expand and the baby to shift into optimal positions for delivery. These movements help the baby navigate the birth canal more effectively, reducing the need for interventions. Forward-leaning and asymmetrical positions, such as kneeling or side-lying, can also encourage the baby to move into a favorable position. Additionally, positions like hands-and-knees can alleviate back pain while promoting baby movement; By staying mobile, women can harness their body’s natural ability to guide the baby through the pelvis, improving labor outcomes. Enhanced mobility not only supports the baby’s movement but also empowers women to take an active role in their labor experience, fostering a sense of control and confidence throughout the process. This approach aligns with the body’s natural rhythms and promotes a smoother delivery.

Specific Birthing Positions for Comfort and Support
Birth balls, forward-leaning, and semi-sitting/asymmetrical positions offer tailored support and comfort during labor, catering to individual needs and enhancing both physical ease and emotional well-being.
Birth Ball Positions
Birthing balls, also known as exercise or peanut balls, are versatile tools that provide comfort and support during labor. Sitting on the ball allows the pelvis to open wider, while bouncing gently can help the baby descend. Leaning forward over the ball can alleviate back pain and encourage the baby to move into a favorable position. Some women find kneeling or straddling the ball helpful, as it allows for gentle stretching and movement. The ball’s flexibility accommodates different body types and stages of labor, making it a popular choice for women seeking non-invasive, natural comfort measures. Regular use of the birthing ball during early labor can also help prepare the body for more active positions later on. Overall, the birth ball is a simple yet effective tool for promoting comfort and facilitating progress during labor.
Forward Leaning Positions
Forward-leaning positions are highly effective during labor, offering both comfort and support. These positions encourage the baby to move into an optimal position for delivery while alleviating back pain. By leaning forward, the pelvis can expand, allowing the baby to descend more easily. Women can assume these positions in various ways, such as leaning over a bed, resting on a birth ball, or even standing and bending at the hips. This stance helps utilize gravity to assist in labor progression and can be particularly beneficial during contractions. Additionally, forward-leaning positions allow for gentle movement, which can help the baby navigate through the pelvis. Overall, these positions are versatile and can be adapted throughout different stages of labor, making them a valuable option for women seeking comfort and support during childbirth.
Semi-Sitting and Asymmetrical Positions
Semi-sitting and asymmetrical positions offer unique benefits during labor, combining comfort and support. Semi-sitting involves reclining in a partially upright position, often with pillows for support, which can help maintain a sense of control while allowing the pelvis to open naturally. This position is particularly useful for women who need to rest while still utilizing gravity to aid labor progression. Asymmetrical positions, such as sitting with one leg raised or leaning to one side, can help the baby navigate through the pelvis more effectively. These positions are especially beneficial if the baby is in a less-than-optimal position, as they encourage the baby to move into a better alignment. Both semi-sitting and asymmetrical positions allow for gentle movement and can reduce discomfort, making them versatile and effective choices for women during labor.
Birthing positions significantly influence labor outcomes, offering benefits like improved comfort, efficient progression, and enhanced fetal movement. Empowering women with informed choices fosters a more satisfying childbirth experience.

Impact of Positioning on Labor Outcomes

Positioning during labor significantly impacts outcomes by influencing pelvic alignment, fetal movement, and comfort. Upright and ambulatory positions can enhance labor progression, potentially reducing the need for medical interventions. Studies suggest that upright positions, such as walking or squatting, increase the pelvic diameter and facilitate fetal descent, often leading to shorter labors. Additionally, these positions may reduce the likelihood of complications like fetal distress or prolonged labor. Forward-leaning and asymmetrical positions can alleviate back pain and improve fetal alignment, further supporting a smoother delivery. Evidence indicates that women who adopt active, upright positions experience less pain and fewer interventions, such as epidurals or assisted deliveries. Thus, strategic use of birthing positions can lead to more favorable outcomes, supporting a natural and empowering birth experience.
Empowering Women Through Informed Positioning Choices
Informed positioning choices empower women to take control of their birthing experience, fostering autonomy and confidence. Education about various birthing positions enables women to understand how different postures can enhance comfort, labor progression, and fetal alignment. By discussing preferences with healthcare providers, women can tailor their birthing plan to suit their needs, reducing anxiety and increasing satisfaction. Knowledge of upright, forward-leaning, and asymmetrical positions, as well as the benefits of mobility, equips women to advocate for themselves during labor. This empowerment not only enhances their physical experience but also strengthens their emotional connection to the process. Informed choices create a sense of ownership, allowing women to feel more prepared and in control, which is key to a positive and fulfilling birth experience.
